2 Chapter 2 Digital Tools and Technologies
Overview
Digital Tools and technologies have many things in common. According to Fredrik Hagstroem and Aigars Macins, digital technologies are vital for artists and designers. They can help artists and designers to create solutions. Digital tools are a domain for creative teams and skilled creators. Digital technologies today can bring constraints and opportunities for the business to operate and serve customers and users over time. Software tools, on the other hand, like builders’ tools, are downed when the creative job is done. A tool’s usefulness depends on how it is used and applied and the artist and designer’s skill level. It is vital that artists and designers need to learn to use digital tools safely and effectively. A tool selection is best made by those who are closest to doing the work. Great professionals will always be curious about new tools and testing out better ways of working for their teams. The best tool is the tool that gets the job best given the combination of the task and the skill of the practitioners.
Digital Tools
Digital tools for art and design encompass both hardware and software applications used to create digital art and artwork for digital production. They provide online learning for students to access such as TinkerCAD, a web application. For creative practice, digital tools provide new opportunities for creative expression and experimentation. They allow students to access a vast amount of information and resources that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to find.
Digital tools consist of 1) design software, 2) 3D modeling software, and 3) animation software. These tools can open up new possibilities for creative expression that were not previously available. These digital tools can help students create digital artworks, animations, and designs that can be shared and exhibited online. Additionally, digital tools can facilitate new forms of creative collaboration, by allowing students to share ideas and collaborate on art projects with classmates and teachers from around the world. Another important way that digital tools can impact art and design education is by providing access to a wider range of resources and materials.
Additionally, digital tools can also make art and design education more accessible to a wider range of students such as students who live in rural areas, older students, students with special needs, and students with language barriers. This can be done by providing online classes, video tutorials, and mobile apps, and creating art education programs that are tailored to different skill levels and learning styles. Digital tools can greatly enhance the art and design education experience by providing students with new opportunities for creative expression and experimentation, and by making art education more accessible to a wider range of students (Sharma, 2022). Moreover, digital tools can help art, design, and digital media students document their learning progress and tell a story about their learning journey and others (Gillespie, 2003).
Digital tools for art, design, and digital media are similar and different in some areas. One of the contemporary software used in the creative industry is Adobe Creative Cloud. According to the NWCT Art Council, there are other digital tools for making art available for students to explore such as Krita, Autodesk SketchBook, MediBang, ibisPaint, and Procreate.
In this course, students will learn to use not only a computer and contemporary software, but also data storage and input and output devices.
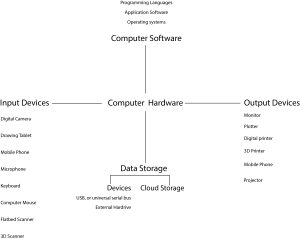
Figure 1 digital tools and devices used to create art and design
Created by Siriporn Peters, 2024
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of logical operations.
- Computer Hardware
There are two types of computer hardware: external and internal. External hardware devices include a monitor, keyboard, tablet, and mouse. Internal hardware devices include motherboards, hard drives, and RAM.
- Computer Software
Computer Software is used to control a computer. Three different types of software run on a computer: system software, utility software, and application software.
System software is designed to provide a platform for other software like macOS, Linux, Android, and Microsoft Windows. Utility software is a program specifically designed to help manage and tune system or application software. Application software or App is designed to help people or users perform an activity.
- Input Devices
Input devices are equipment used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system, such as a computer or information appliance. Examples of input devices include a keyboard, a computer mouse, a tablet, a scanner, a camera, a microphone, and a mobile phone.
- Output Devices
Output devices are computer hardware devices that retrieve and present the result of the inserted input data from the computer system and further translate that data into human-understandable language. The output or result is then presented to us in the form of text, visuals, audio or a hard copy (printed on paper). The output devices can be mainly classified into four categories such as visual, data, print, and sound. Based on the type of output and requirements, different output devices can be attached to the computer systems to retrieve the output
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speakers
- Headphones
- Projectors
- GPS
- Plotter
- Braille Embosser
- Haptic Devices
- 3D Printer (Aparna, 2024)
- Storage Devices
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. There are 5 different
- USB drive.
- Hard Disk.
- Floppy Disk.
- Compact Disc.
- Cloud Storage
Digital Technology
Digital technologies are powerful tools that can help improve education in various ways, such as making it easier for instructors to generate instructional materials and providing new methods for students to learn and collaborate. Moreover, digital technologies have continued to play an essential role in delivering education to students both inside and outside the classroom. Digital learning fosters creativity and gives students a sense of success, encouraging additional learning by thinking outside traditional techniques (Haleem, et. al. 2022).
Digital technology is an electronic system and resource that helps us learn, communicate, play, and more. Digital technologies include:
- Computer
- Smartphones
- Smart TVs
- Online games
- Video on demand websites
- Traffic lights and pedestrian crossings
- Automatic doors (BBC).
Digital tools and technologies for art and design have been rapidly developed to help art and design practitioners in higher education and creative industries to speed up their work flow and produce new art and design. Digital tools and technologies are developed to help the art and design practitioners to explore various creative solutions and prepare artwork for digital production effectively.
Further Readings:
Hagstroem, F. and Macins, A. (n.d.). Don’t confuse tools with technologies.
Sharma, B. P. (2022). Digital tools in art education: From expanding creative horizons and facilitating collaboration to increasing access and resources for a diverse student population. Applied Research in Artificial Intelligence and Cloud Computing, 5(1), 55-65.
Lane, A. (2019). What is Technology?
Teal Labs. (n.d.) What tools do art teachers use?