1 Chapter 1. DEVELOPING AN IDEAL SPORTS ORGANIZATION
Steve Shih-Chia Chen
Learning Objectives
*Understand the importance and benefits of becoming an employer of choice
*Recognize the quality and needed leadership styles for becoming a good employer
*Understand the employees’ expectations and needs in order to foster an effective and productive working environment
*Understand and describe the steps that must be taken to develop an ideal corporate culture
Becoming an Employer of Choice
Regardless the size of one’s company or organization, an “employer of choice” is an employer that attracts, optimizes and holds top talent for a long tenure (HBR, n.d.; Sawyer, 2001). The employees will make a conscious decision and choose to work for their ideal employer when presented with other employment opportunities. This mentality of becoming an “ideal” boss can be practiced in any size organization. Due to the competitive nature and challenges for allocating additional resources in the industries, employers must understand and face the reality that employees will have a powerful tool, choice, while seeking employment (Jackson, 2014). Top candidates with unique skills are in short supply. What can an employer offer to help workers choose to work for his/her organization? This is why having the brand of “employer of choice” is extremely vital and attractive in recruiting. There are numerous advantages and benefits for an individual choosing to be an ideal boss and employer of choice (Herman & Gioia, 2000). Some of the advantages include:
(1) having easier recruitment,
(2) being able to choose the best of the best,
(3) ensuring high loyalty and low turnover rate,
(4) maintaining high productivity and efficiency, and
(5) obtaining a great reputation and staying attractive to investors and consumers.
It is every employer’s dream to establish a successful organization during one’s tenure. In order to achieve that dream, experts suggest all employers to become an “employer of choice.” As the nation’s economy rises and falls like a roller coaster, employment opportunities and rates also fluctuate. It is a crisis that many educators worry about as more graduates ready to enter the workforce not assured of their chance for getting hired soon. Surprisingly, with lots of employees looking for jobs, many employers still have difficulty in recruiting and retaining employees and complain about the worker shortage. The results of employee benefits in the workplace survey showed that the employers often failed to utilize relevant incentives to entice potential job candidates. Examples of these types of incentives may include items such as wellness initiatives and flexible work arrangements. With wages holding fairly steady since the 2008 recession, employers could do well by offering great benefits as a “total rewards” approach to attract top talents. It was noted that well recognized “employers of choice” often have been successful in developing family-friendly programs and corporate culture. According to the Department of Labor, it costs a company 1/3 of a new hire’s annual salary to replace a leaving employee. This shows the importance of hiring and retention of a good employee (Sawyer, 2001). Past studies have shown it is not costly at all to develop family-friendly programs (roughly about 2.3% of employees’ salaries). Since many job candidates and employees have longed for family-friendly workplaces, many renowned companies are integrating work/life initiatives into their corporate culture. The COVID-19 pandemic has further taught the employers an important lesson. They need to offer a sense of mission and respond to the environmental changes and employees’ demand I order to shape the future (Delaney, 2021). Readers can refer to Table 1for information concerning work/life initiatives among best companies to work for in America according to Indeed.com.
Table 1. Examples of work/life initiatives among best companies to work for in America.
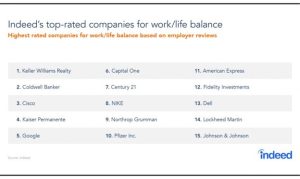
[1] Best Places to Work for Work/Life Balance by Indeed.com
http://blog.indeed.com/2018/04/24/best-places-to-work-work-life-balance/
| FYI: 2017 Best Places to Work
Top companies in Kentucky: SHRM: Headquarter based in Alexander, VA, one of Washingtonian magazine’s Great Places to Work for 2013 and many others have offered examples of best practices that make one’s company to be “an employer of choice.” (Roberts, 2011) *Rewarding employees with fair and competitive compensation and benefits; *Offering meaningful work and creating a challenging and interesting work environment; *Monitoring great work/life balance; *Offering training and professional development opportunities; *Inspiring employees with great managers and leaders; *Recognizing and respecting employees; *Maintaining financial stability; *Committing to charity and community; and *Creating an ideal culture.
More information on traits of being an attractive employer (published on 19, 2011) According to Breeman, an analyst of Edward Jones, here are 11 great things that companies among the list of100 Best Places to Work have done. 1. Offer a flexible work schedule; 2. Make the workplace kid-friendly; 3. Foster a culture that is creative and fun; 4. Cultivate the whole person; 5. Don’t tolerate jerks; 6. Reward great customer service; 7. Understand people have lives outside of work; 8. Establish a mission inspires people to do their best; 9. Listen to the employees; 10. Have a good incentive program; and 11. Pay a decent wage.
FYI: Best Country to work at according to the ranking by IMD (2011)
|
Understanding the employees’ expectations and needs
In sport marketing, knowing the needs and wants of the consumers is considered the most important priority in providing great and successful service. Employers must remember that “people” (employees) are the most valuable resource for any corporation or organization (Sawyer, 2001). Therefore, their concerns and requests can often be critical factors that influence their commitment, loyalty and satisfaction with the organization (or the employer). The authors would use the acronym (6Ps) to characterize the concerns that are cared about by both employees and employers.
(1) Pay: This is the primary benefit that employees care about the most. On the other hand, revenue generation is not a simple task. While the organization is generating the revenue through the work and dedication of its workers, the employer may still naturally think about suppressing the workers’ salaries and try to cut down any of the unnecessary spending regarding employee benefits.
(2) Pride: Being a professional is not just about earning a paycheck. All employees want to have a meaningful and enjoyable job that makes them proud and happy. Employees want to work for a reputable and well-respected organization. In the meantime, the employers would like their employees to take pride in their organization. Having a great image and professional reputation is certainly an important element that the employer strives to achieve for his/her organization.
(3) Passion: Passion is the driving force that keeps people motivated, working hard, and loving their job. Without passionate workers and leaders, the organization will lose its vitality and enthusiasm to make any progress. When employees are bored and lose interest in their job, it makes no sense for them to continue their work. Therefore, the employers must create a friendly and enthusiastic corporate culture to foster employees’ passion towards their job and life.
(4) Performance: This element is the most predominant indicator of the organization’s survival and success. When employees perform well, this will benefit them in earning higher salaries and boosting their work morale. However, the employer will be the biggest benefactor, if his/her employees achieve excellent performance then greater productivity will be reached.
(5) People: A serious complaint that employees may have in the work setting is “don’t make me work with an idiot.” (Burn2, 2010). This shows how important it is for an organization to have employees with high quality characteristics working together as a team. It is essential and fundamental for the employers to hire and retain these quality individuals, so the organization can function smoothly. People are drawn to good leaders. Leaders are the breakers or makers who will dictate the success of the company, since they are the ones who set the tone, influence corporate culture, and hire the people to do the job. So employers must build a trustful and collegial relationship with their employees to function as a team.
(6) Place (Environment): Maslow has indicated that having food and safe shelter is the basic human need. It is no surprise that employees will demand a safe and friendly work environment from their employer.
In the article “12 things we’d tell our bosses if we could,” Burns (2010) highlighted many intricate details that an employer may need to emphasize and execute to make the employees feel respected and nurtured. This means the employer will need to go above and beyond to care about employees’ needs and expectations and help them perform and grow while performing on their job. Several suggestions along with advices were given by Burns (2010), Strauss (2011), Rehn (2015), Roberts (2011), and Barker (2014) with regard to being an ideal employer. Employers must offer the adequate training, supervision, resources, authority, respect, and tools to execute their tasks. Employers need to offer clear vision, guidelines, instructions, communications, and feedback. They must walk the walk by actually leading the employees to do their job, not merely giving the order or instructions. Employers must consistently praise their employees for their good performance, and be a buffer when conflicts occur between employees. If possible, they should mentor their employees in every possible way to develop their employees professionally. When employees make a mistake, they need constructive criticism and second chance to get things right, not getting scolded or neglected. More importantly, the leaders must act consistently and honestly and learn to listen for opinions.
Perfectionism is not so perfect
There are also certain pitfalls that a good employer must avoid in their desire to ensure the employee remain happy and productive (Hyacinth, 2016). First, the employer must stop micromanaging. In addition, employers cannot lack empathy and they must provide opportunities for growth and development for their employees. Obviously, failing to support work/life balance and neglecting employees’ efforts are like devaluing the employees’ contribution that give them reason to leave the organization.
Often time, we’ve thought that striving for perfection was the key to productivity and profit. In reality it is the opposite. Perfectionism affects 92% of workplace people including the leaders, the bottom line workers and even one’s organization culture. Symptoms of perfectionism may include unrealistic expectations, fear of failure, procrastination, micro-management, people-pleasing, self-criticism, conflict avoidance, feeling stuck, imposter syndrome, indecision and anxiety (Hardin, 2022). These symptoms are hindering the organizations’ leaders and workers in a negative way. According to a research study by the University of Northern Colorado, 86% of leaders believe their work is impacted by these perfectionist mentalities or practices. Examples of the effects of perfectionism can be found all over the places. For examples, the boss would cross work/life boundaries and ask his/her workers to work overtime. Employees struggle to say no to unrealistic expectations and timelines. Managers are afraid of failure and scared to take any risk for innovating ideas and plans. Eventually, these perfectionist symptoms will create a lack of trust, collaboration, efficiency, openness, accountability, clarity and adaptability in an organization (Hardin, 2022). To minimize the impact of these symptoms, leaders may take following steps: (1) building awareness and offering education on the issues, (2) examining your organization’s culture and practices, and (3) implementing leadership development and training programs to correct perfectionism problems. The goal is to build a workplace of excellence, not striving for perfectionism.
Corporate Leadership
The key to becoming an “employer of choice” is commitment from the top leader. The employers must commit to the concepts, practices, as well as necessary resources to make it a reality. Many experts encourage employers to adequately inspire their employees (Roberts, 2011). Most employees do not leave a company; they quit their manager. Therefore, it is critical to invest in hiring and training great managers (Roberts, 2011). Organizations that are viewed to be “employer of choice” often are credited with having a family-friendly corporate culture and inspiring leaders and managers. Leaders and managers are usually the movers and shakers that make a difference every day in their decisions, actions, and their interactions with fellow employees. They are the individuals who hold the position and resources to make things happen. Many studies address the leadership styles, qualities, and characteristics associated with leaders that explain how these individuals can perform effectively and successfully in guiding their subordinates (or employees).
According to John Gardner, leadership is the process of persuasion or example by which an individual induces a group to pursue objectives held by the leader or shared by the leader and his or her followers (Rehn, 2015). In general, leaders are encouraged to adopt a democratic leadership style to foster group participation, intergroup communication, creativity, and interaction. However, under special circumstances (i.e. employees are inexperienced, not enough information or time for group members to form discussion, accountability is great for any others to bear), the leaders may need to step up and choose the authoritarian style to make quick decisions. When employees (or subordinates) are talented, knowledgeable, and enthusiastic, it may be a great idea for the employers (or leaders) to take a laissez faire approach, so the employees can experience more autonomy, independence, and freedom. In reality, there is probably no one universal ideal leadership style or the one-size-fits-all style that works for all cases or situations. So leaders may take the eclectic approach by blending in many different styles and carefully choosing the most appropriate style to deal with encountering situations.
Regardless of the leadership style that an individual may act on or carry out, there are preferable characteristics and traits that employees would love their bosses to exhibit (Strauss, 2011). In general, employees would like their employers to be both future oriented and people oriented. Employers must demonstrate visionary leadership. They must provide effective communication, positive encouragement, and sincere and honest feedback. Employers need to show great enthusiasm, accountability, compassion, understanding and sensitivity. They must reduce organizational conflicts and politics, and cannot tolerate jerks. They also need to learn to be a great listener. Of course, there are more items that can be listed.
| FYI: Common leadership styles among Corporate America (Rehn, 2015)
Visionary- This type of leadership was perfectly defined by Steve Jobs, and his name will most likely always be associated with it. To be a visionary leader, one must be willing to experiment, take risks, and make changes in order to reach his/her goals. Coaching- The coach will reach out to individual employees by helping them develop professionally and make entire team reach its goals. Democratic- Democratic leadership requires the participation of the entire work team, and every vote counts. However, gaining consensus based on the views of the majority is not always time- and cost-effective. Commanding- This is the more traditional approach to leadership, involving one leader, or a leadership team, taking charge of the office. Common characteristics demonstrated by good leaders (Rehn, 2015; Sawyer, 2001). Being future-oriented Being people-oriented Being visionary Fostering communication Offering encouragement Providing feedback (with sincerity and honesty) Assuming accountability Reduce conflicts and politics Demonstrate enthusiasm Respect seniority And of course, there are more!! |
The intent of this section is not about looking for or breeding a perfect employer, it is about helping readers understand that there are clear strategic advantages to be a good employer favored by employees. The leaders and employers must realize that the most valuable resource of an organization are the employees, the human capital. When employers exhibit and demonstrate preferable leadership characteristics and qualities, the talented employees will be drawn to them. As a result, these popular employers will get to work with the most qualified and passionate workers and obtain the benefits of their loyalty and productivity.
| Video Clip: Create a Mentally Healthy Workplace and Become an Employer of Choice (by Heads Up Australia) |
How to build an ideal organization?
Each organization has its own unique culture. In other words, there is no one particular “right” way to run and develop a corporate culture that fits all the employees. Employees have choices, so they select the employers and culture that are most comfortable for them. Despite the notion of there is no universal ideal way to run a perfect workplace, there are still common characteristics that are suggested for implementing a family-friendly workplace. Examples of these characteristics include (Baker, 2014; Boutelle, 2013; Brooks, 2015; Hyacinth, 2018; Matuson, n.d.; Merchant Pro Express, 2016; Rehn, 2015; Strauss, 2011; Unkonwn, n.d.):
(1) Creating and maintaining a unique culture;
(2) Establishing values and standards;
(3) Developing strong internal support structure;
(4) Providing proper access to information;
(5) Building a culture of success;
(6) Designing a successful communication system; and
(7) Maintaining and honoring rituals and traditions.
The caring employer will also do the following:
- (1) refine the concern about quality of life to concentrate on quality of work life;
- (2) build fun and variety into work experiences; and
- (3) create an environment that invites people to want to come to work.
Clearly, it is important to recognize the impact that a family-friendly corporate environment may have on employees. Readers may wonder how to improve or build a great corporate environment. The primary tasks are focusing on attracting, optimizing, and holding good people. Organizations are composed of people. When an organization attracts and retains good people to work with each other, then strategies and practices will become more meaningful as they are adopted to build a good corporate environment (see Table 2).
Table 2. Examples of strategies and actions for improving corporate environment (Herman & Gioia, 2000)
| Advocate work/life balance |
| Demonstrate respect for all individuals |
| Support employees with great safe environment, benefits, flexibility, and convenience |
| Adopt proper technology for the employees to do the work |
| Maintain great relationship by connecting with employees’ family and friends |
| Support simplicity, make it easy to get things done for employees. |
| Stage events such as employee appreciation, employee travels |
| Foster communication with technology |
| Establish reward and promotion system (recognizing milestones, special occasion, and internal promotion) |
Human Resource Development
As able job candidates are recruited, ongoing job-skills training needs to be introduced and accommodated to help the employees learn and perform their jobs well. Training will help employees attend to specific, detailed, and routine job skills, techniques, and technologies. Development should also be encouraged by the employers and managers to promote growth of ability, attitudes, and personality traits. In general, human resource development begins with the new employee orientation. Orientation is also the first step of job training. The primary goals and benefits of orientation are to: (1) reduce errors, turnover, anxiety, and adjustment time for the new work, (2) instill more positive work values, (3) increase productivity, and (3) improve motivation and satisfaction.
On-the-job training (OJT) is the most commonly used method of employee training. New employees are usually coached and guided by the experienced supervisor. They should be placed at the appropriate level and environment to perform the work. Plans for advancement and job rotation should also be designed and prepared to further develop the employees.
In sports settings, apprenticeships or mentorships are common practices that allow supervisors to instruct and guide their trainees to acquire task skills or knowledge through a period of interactions. Vestibule training aims to provide opportunities for the employees to use new equipment, machines, and technology. Organizations also can conduct a series of programmed learnings by using film, printed materials, or online training modules. Learners can go over the teaching materials at their own pace and time. Certificates of completion or achievement can be given to those who successfully complete the training courses as well as be placed in their personnel file.
Studies have shown that new employees who went through orientation program are more likely to be with the company three years longer than those who did not attend. Employers also need to realize that orientation is not just about giving instructions, trainings, and policies to the employees, but it is also an opportunity for the employees to learn about the company and to test the compatibility between the employees and the organization. So employees may get the chance to ask for things like difficulty of the task, preventive measures and safety of work environment, method of evaluation, and friendliness of leaders and coworkers.
| Video Clip: 10 Skills to Train Employees – Employee Training and Development |
When preparing for the orientation presentation, the following important pointers have proven to be useful:
- Create a good first impression;
- Provide the explanation and instructions on purpose and format of the orientation;
- Describe the organization’s culture, rules, policies, and procedures in details;
- Emphasize accurate information will be delivered and proper communication processes will be executed;
- Ensure the organization will commit to train, evaluate, and promote employees on a long term basis;
- Establish friendly relationships among workers and help employees to adapt to their surroundings quickly;
- Reinforce the employees’ decision to join; and
- Prepare training packets, DVDs, and video materials and make them available for the employees
| FYI: Popular On-the-job Training in Higher Education Setting and Collegiate Athletics
*Teaching strategies and coaching clinics: *Technology training: Use of software programs, analytics, Excel, social media, and many more *Diversity and Inclusion: *Sexual harassment: *Human resources and policies: *NCAA compliances and policies: *Cybersecurity training: |
Conclusions–Getting Started in Becoming an Employer of Choice
We all know that knowing how and doing so are two completely different things. Becoming an Employer of Choice is a self-interest and bottom-line issue (Sawyer, 2001). If an organization wishes to achieve excellence, it must have total commitment coming from the top-level executive down. The stability, strength, and future of the organization will all be critical elements that must be closely reviewed. Top executives and management teams must discuss the Employer of Choice concept and buy-in to this ideology. The employer must be willing to be a servant-leader. The organization must develop mid-level managers in order to build a close relationship with their people (subordinates). Managers will need to review internal records and perform evaluations periodically. In addition, the organization must market the value and practice of internal promotion. If the organization can treat its employees as well as or better than it treats customers (or clienteles), the organization will achieve enviable results.
Quiz Questions
Q1. Reasons for being an “employer of choice” may include:
- Recruiting employee will become considerably easier
- Enhancing loyalty
- Planning for continuity
- All of the above
Q2. Many studies had shown that the total cost for developing family-friendly programs by the employee services department is about 40% of the total cost of employees’ salaries. True/False
Q3. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a caring employer?
- build fun and variety into the work experience
- create an environment that invites people to come to work
- cutting the budget of the family programs
- refine the concern about quality of life to concentrate on quality of work life
Q4. Which of the following is incorrect?
- Training usually begins with evaluation.
- Human resource development starts with the orientation of new employees.
- On the job training is the most frequently used method of training new employees.
- An effective orientation program can reduce labor turnover.
Q5. Employees who attend an orientation program are more likely to be with the company three years later than those who did not. True/False
Q6. The employers often need to spend a lot of money to come up with an effective motivating reward. True/False
Q7. Which of the following is not a problem that a good employer may wish to avoid?
- Micromanaging all the time
- Lack empathy
- Actively support work/life balance
- Neglecting employees’ efforts constantly
Q8. Please identify at least two useful pointers for preparing an orientation presentation. (short answer question)
Brainstorming Activity
How do I tell my boss I want a certain position? (Try to answer this Dear Abby-type of letter)
Dear Abby,
I had a lunch with my coworker in a local restaurant last week. During the lunch, I overheard a conversation between my boss, the Athletic Director, and a major donor of our athletic program. I am 99% sure that he was talking to the donor about the potential vacancy of the Director of Media Relations in our department. My boss mentioned the idea of conducting an external search for the position. Apparently, he was not aware that I was in the restaurant.
I want to tell my boss that I am really interested in applying for that position. As the Assistant Director of Media Relations for the past four years, I think I am well qualified and ready for this promotion. Is there any polite way for me to address this with him, so he could cancel the idea of having an external search? Would he be upset with me, if it sounds like I had listening his conversation behind his back??
In case you (as Abby) are suggesting the applicant to prepare an employment cover letter, you may check out the following useful documents.
Resume Now. (n.d). Professional employee cover letter sample & writing guide. https://www.resume-now.com/cover-letter/examples/human-resources/employee?utm_source=bing&utm_medium=sem&utm_campaign=361052460&utm_term=resume-now&network=o&device=c&adposition=&adgroupid=1188572922523359&msclkid=0e887bd151b61228b3551a5d07f6e71d.
Writing, L. (2020, February 25). Writing an effective job request letter- sample, example & tips. Letters.org. https://www.letters.org/request-letter/job-request-letter.html.
Interview Tips
https://www.youtube.com/user/The2InterviewGuys?v=qSylCmes5dw
| Food for Thoughts(by Adina Joseph)
While you contemplating the brainstorming activity, please take a moment to consider this question as well. This question is often the most dreaded question by most job seekers. “Why should we hire you? How on earth can an applicant respond this question adequately?? Please think through these elements carefully!! 1) Answer with a positive tone and show enthusiasm; 2) Preparation; 3) Highlight experience; and 4) This is time to sell yourself!! Madkour, A. D. (2013, August 26). What to look for in making the right hire: 8 executives offer key tips. Street & Smith’s SportsBusiness Journal, 16(19), 18-19. Here are tips offered by top sports executives about identifying the right candidates to hire: John Martin (NASCAR): Look for stability Eric Woolworth (Miami Heat): Adapt to the culture Brian Grey (Bleacher Report): The right fit Pete Guelli (Charlotte Bobcats): Strong work ethic Derek Aframe (Octagon): Take group approach Mark Hollis (Michigan State): Ask surprise questions David Simon (LA Sports Council): Demonstrate strength Chris Zimmerman (Bonfire Group): Show passion |
Image Citations
[1] Photo courtesy by Creative Commons 3 – CC BY-SA 3.0, under public domain
https://www.flickr.com/photos/mypubliclands/15163291590
[2] Photo Courtesy by U.S. Department of Defense, under public domain.
[3] Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons, under public domain.
References
Baker, T. (2014). The eight values of an employer of choice. https://www.trainingjournal.com/blog/eight-values-employer-choice
Boutelle, C. (2013). Psychology of leadership: A cure for collapsing confidence in leaders. SIOP Public Relations. http://www.siop.org/article_view.aspx?article=1195
Brooks, C. (2015). Servant leadership style is best for bosses. Business News Daily. http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/7964-best-leadership-style.html
Burns, K. (2010). 12 things we’d tell our bosses if we could. US News. http://finance.yahoo.com/news/12-Things-Wed-Tell-Our-Bosses-usnews-1082890159.html?x=0
Delaney, K. (2021, August 2 & 9). We’re in a bold new era at work. Time 198(5-6), 47.
Hardin, V. B. (2022, December 12). Research: The negative impact of perfectionism in the workplace. https://www.lanereport.com/161400/2022/12/research-the-negative-impact-of-perfectionism-in-the-workplace/?utm_source=Faster%20Lane%20Newsletter&utm_medium=Email&utm_campaign=
HBR (n.d.). Employer of choice. https://hbr.org/resources/pdfs/comm/siemens/hbr_siemens_report.pdf
Hewitt (2009). What makes a company a best employer? http://www.aon.com/attachments/thoughtleadership/pov_Best_Employer_Position_Paper.pdf
Hyacinth, B. (2018). Five things that make good employees quit. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/5-things-make-good-employees-quit-brigette-hyacinth/?trk=eml-email_feed_ecosystem_digest_01-recommended_articles-8-Unknown&midToken=AQH81IFbXncN1A&fromEmail=fromEmail&ut=0s0KPuZqxdwU81
Jackson, H. G. (2014). Becoming employers of choice. HR Magazine. https://www.shrm.org/hr-today/news/hr-magazine/pages/0314-ceo.aspx
Matuson, R. (n.d.). Effective leadership styles that inspire performance. https://hiring.monster.com/hr/hr-best-practices/workforce-management/hr-management-skills/leadership-styles-that-inspire.aspx
Merchant Pro Express (2016). 9 qualities of a good employer. http://news.merchantproexpress.com/9-qualities-of-a-good-employer
MSG Management Study Guide (n.d.). Leadership styles. http://managementstudyguide.com/leadership-styles.htm
Rambe, P., & Dzansi, Y. D. (2016) Informal distributed leadership in technology adoption. African Journal of Science, Technology, Innovation and Development, 8(2), 155-165.
Roberts, G. (2011). What it means to be an ‘employer of choice’.
http://www.virginiabusiness.com/news/article/what-it-means-to-be-an-employer-of-choice
Rehn, K. (2015). Four leadership styles and their potential impact on your workers. http://hhstaffingservices.com/what-your-leadership-style-says-permanent-and-temporary-employees/
Sawyer, T. H. (2001). Employee services management: A key component of human resource management. Champaign, IL: Sagamore.
Strauss, S. (2011). 11 Traits of a great employer. Strauss Group Inc. https://www.americanexpress.com/us/small-business/openforum/articles/11-traits-of-a-great-employer-1/
Unknown (n.d.). Leadership styles: Choosing the right approach for the situation move this behind. https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newLDR_84.htm
